Hazardous Area Classification for Ships & Offshore Safety
Understanding Hazardous Area Classification on ships and offshore installations is paramount for preventing catastrophic incidents. In environments where hydrocarbons are processed, explosive gas atmospheres are a constant threat. This crucial process identifies and maps areas where flammable vapors can mix with air, forming a dangerous cocktail, and forms the bedrock for safe design and operation in the marine and offshore sectors.
Why Hazardous Area Classification is Essential for Safety
This classification goes beyond simply marking danger zones; it directly influences the entire design of a vessel or platform. From how cables are routed to the placement of ventilation inlets and the specific type of electrical and mechanical equipment installed, every decision hinges on proper classification. The goal is to mitigate risks from potential ignition sources like sparks or hot surfaces, safeguarding personnel and assets by preventing explosions.
Understanding Hazardous Zones and Equipment Levels
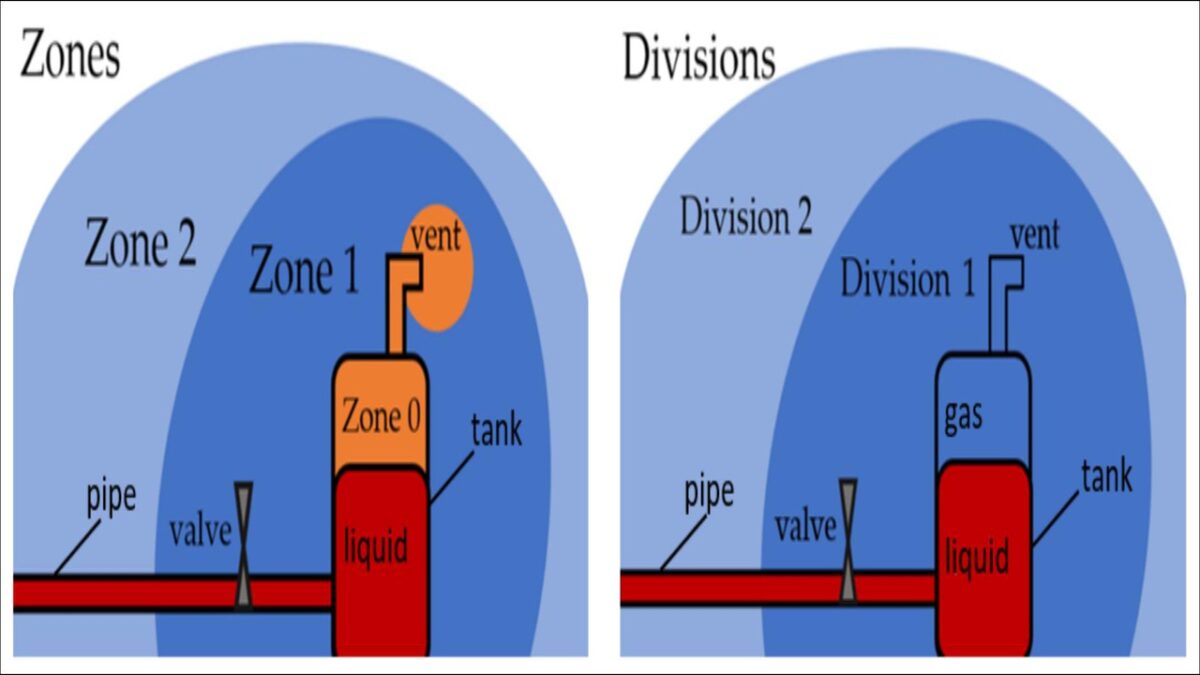
International standards, such as IEC 60092-502 and IEC 60079-10-1, define a zone system to categorize hazardous areas based on the frequency and duration of an explosive atmosphere. For instance, Zone 0 denotes areas where an explosive gas atmosphere is present continuously or for long periods, demanding the highest Equipment Protection Level (EPL Ga), often through intrinsically safe circuits. Zone 1 represents areas where an explosive atmosphere is likely to occur in normal operation. Adhering to these classifications ensures that only suitably protected equipment is used, enabling safe maintenance and operations across all maritime and offshore facilities.